Genre and Artist Recognition
PANDORA project
Older project: It has been showed that different elements of visual art such as shapes, colors, and boundaries are processed by different pathways and systems in the brain, designed to interpret each aspect of the art and there is no single central mechanism that receives and interpret visual art, but instead, pieces of information received from a painting are selectively redistributed to more specialized centers for processing.
For the specific painting classification we have constructed a system addressing each of the main perceptual categories: shapes (anchors from the Gestalt theory), color (as minimum enclosing elipsoid of the 3D Lab histogram) and edges (using Gabor wavelets).
Eye center localization
We have introduced ZEP feature formed by TESPAR encoding of image projections. It turned out that, beside the ease of computing, they are very good at describing the eye region and thus to eye center localization.
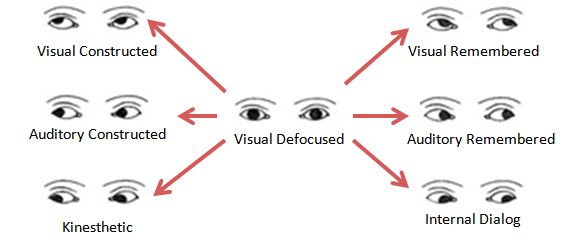
Recognizing Eye Accessing Cues
Eye Accessing Cues (EAC) model is the part of the Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) theory that describes the eye-movements that are not used for visual tasks and suggests that the direction of gaze can be an indicator for the internal representational system used by a person, who may think in visual (i.e. images), auditory (sounds) or kinesthetic terms (feelings), as well as for the mental activity of that person, of remembering, imagining or having an internal dialog.
Eye-Chimera Database
Eye-ChIMERA (EYE part from the Cognitive process Inference by the Mutual use of the Eye and expRession Analysis)
database has been constructed specifically to test algorithm discrimination power in the 7 gaze situations named
in the EAC-NLP model. Frames extracted are the relevant ones from videos recorded either with Canon 600D
(640 x 480 resolution), either with Panasonic HDC-TM 60 (1920 X 1080) cameras on 40 subjects in the 20-30 age range.
Illumination is typical-indoor and the light comes from one side. The subjects were asked to follow specific movement patterns
and the significant frames were cropped out. The five eye landmarks named in [this]
paper are manually marked by three experienced annotators and their average is reported as ground truth. The landmarks markings
are delivered with the database. Furthermore, the images have been grouped in 7 gaze direction cases.
By getting the database, one implicitly acknowledge that he/she will agrees to the conditions specified :
[here]
The database can be downloaded from this [link] .
Face description using HoT
HoT (Histograms of Topographical features) assume gray-scale images as 2-dimensional surfaces and their approximation in Taylor series. Beside the popular Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HoG), we show that both magnitude gradients and surface curvature, expressed with respect to local Hessian eigenvectors orientation and eigenvalues magnitude, carry supplementary information that ease face description process.
The Logarithmic Image Processing (LIP) models are part of a larger category of non-linear image processing techniques that were introduced for overcoming limitations image processing techniques based on real operations. Due to their rigorous mathematical properties and similarities with human visual system, many application have appeared.
Here, we have contributed by:
- Discussing the general mathematical framework. Some details may be found in chapter 2 of this work
- Image enhancement (see this paper) and focussing (this paper) based on LIP technique
- Digitization of analog radiographs
- Processing of cellular images
- Amplifying underexposed images
- Constructing HDR images. More details in the arXiv paper.